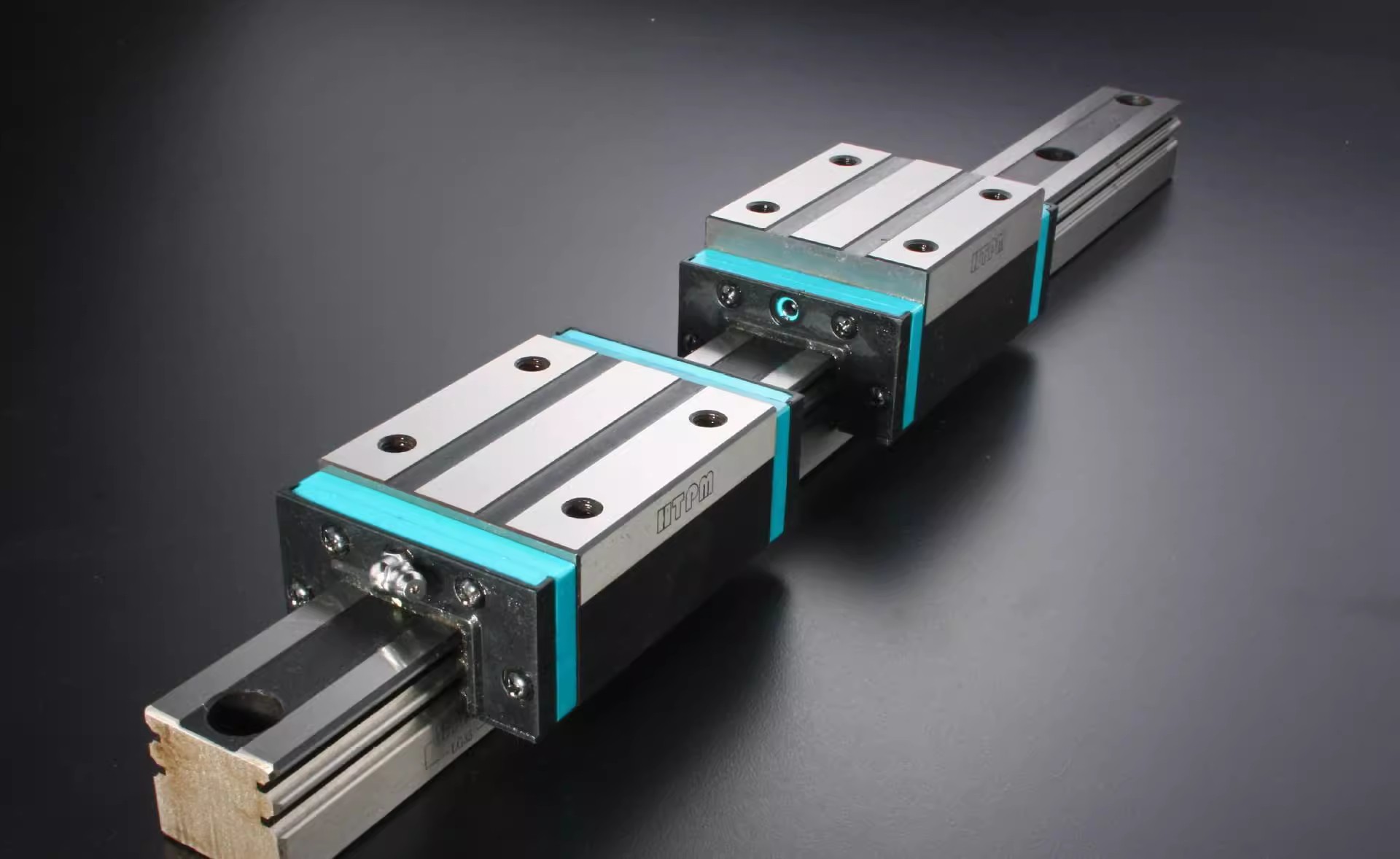
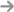THK Linear Guide Selection Guide
Publish Time:
2025-02-25
In the field of modern mechanical manufacturing and automated equipment, linear guides, as key components, directly impact the equipment's operational precision, stability, and service life. With a wide array of linear guide products on the market, accurately selecting products that meet specific needs has become an important issue for engineers and equipment purchasers. The following will elaborate on the key points of selecting linear guides from multiple core dimensions.
I. Clarifying Application Scenarios and Load Characteristics
Working Environment Analysis: Different working environments have different requirements for linear guides. In dust-sensitive environments such as clean rooms, linear guides with good dust-proof and sealed designs should be selected, such as models equipped with special dust covers or sealing strips, to prevent fine particles from entering the guide, affecting precision and lifespan; in high-temperature environments, such as some heat treatment equipment, the high-temperature performance of the guide must be considered, selecting products made of high-temperature materials (such as special alloy steel) and lubrication systems that can adapt to high-temperature conditions, ensuring stable operation at high temperatures.
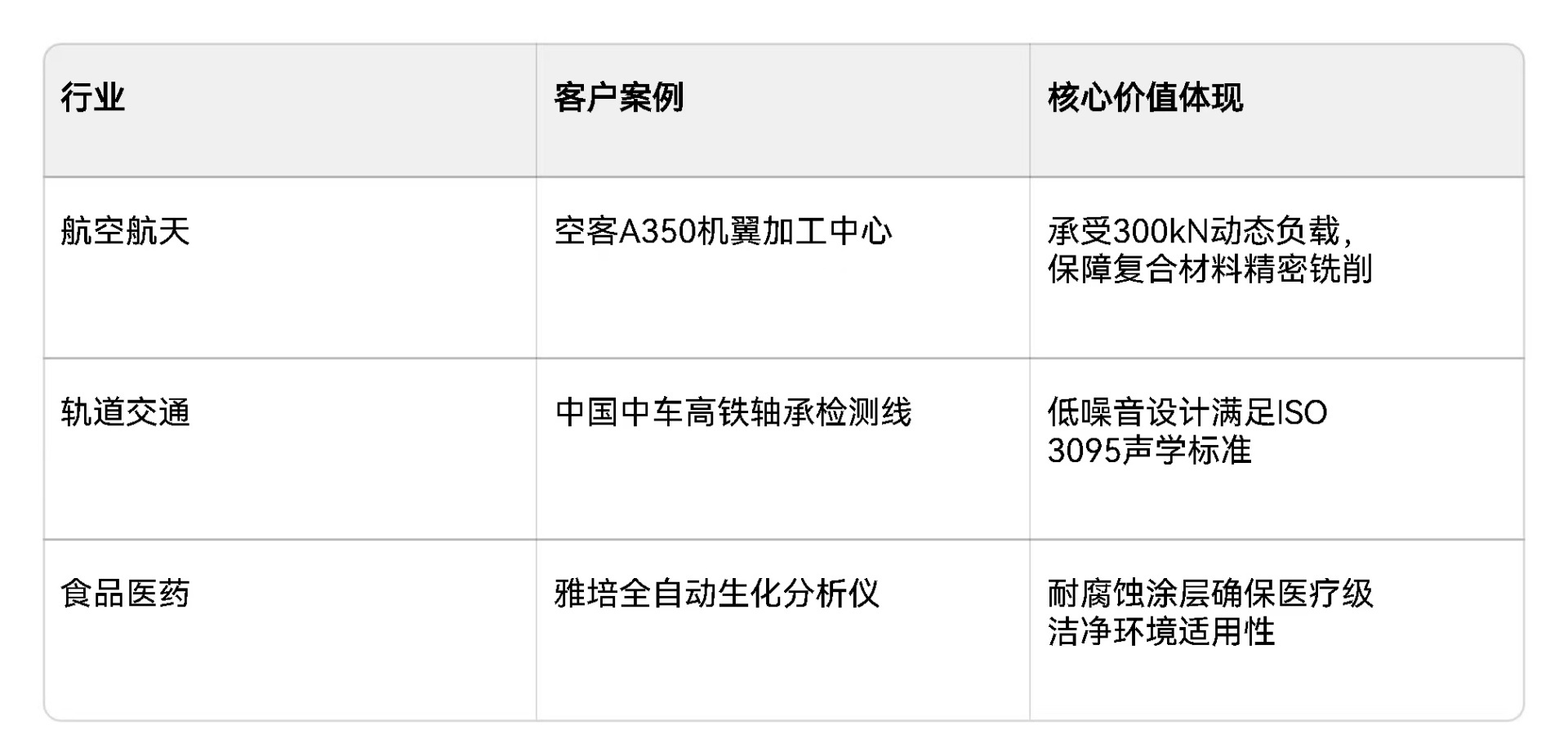
Load Type and Size Determination: Accurately assessing the load type (including static load, dynamic load, and impact load) and size is the basis for selection. If the equipment mainly bears a constant static load during operation, a guide with a rated static load greater than the actual load can be selected according to the load weight; if frequent starts and stops, acceleration and deceleration, etc., generate dynamic loads, the dynamic load capacity becomes a key consideration, and the rated dynamic load of the guide must meet the needs of long-term operation; for applications that may encounter impact loads, such as stamping equipment, the selected guide must have sufficient impact load capacity, and the impact load parameters in the product sample can usually be referenced, and the selection can be made in conjunction with the safety factor.
II. Precision Grade Matching
Precision Grade Classification: Linear guide precision grades are generally divided into ordinary grade (C), high grade (H), precision grade (P), ultra-precision grade (SP), and ultra-high precision grade (UP). Ordinary grade is suitable for general conveying and supporting occasions with low precision requirements, such as some simple material handling equipment; high-grade and precision-grade precision is gradually improved, suitable for machine tool processing, automated testing equipment, etc., which can ensure high positioning accuracy and repeat positioning accuracy; ultra-precision grade and ultra-high precision grade are mainly used in fields with extremely strict precision requirements, such as semiconductor manufacturing equipment and optical testing instruments, which can achieve high-precision motion control at the micrometer or even sub-micrometer level.
Balancing Precision and Cost: Although high-precision linear guides can provide excellent performance, they often come with higher costs. During selection, the precision requirements and budget constraints of the equipment should be considered comprehensively to avoid excessive pursuit of high precision and resulting in cost waste. For example, for some automated production lines that are cost-sensitive and have precision requirements around ±0.05mm, selecting high-grade precision guides can meet the needs, ensuring normal equipment operation while keeping costs within a reasonable range.
III. Guide Size and Installation Method
Guide Size Determination: Guide size includes guide width, slider size, etc., which needs to be determined based on the equipment's spatial layout and load conditions. In equipment with limited space, compact size guides, such as miniature linear guides, should be selected to save installation space; for applications carrying larger loads, guides with wider widths and larger slider sizes should be selected to provide sufficient carrying capacity and stability. At the same time, it should be noted that the length of the guide must meet the travel requirements of the equipment, and when calculating the length, the installation margin and reserved compensation space should be considered to prevent the guide from being obstructed due to thermal expansion and contraction.
Installation Method Selection: Common installation methods for linear guides include bottom installation, side installation, and top installation. Bottom installation is the most commonly used method, suitable for most equipment, with stable installation and easy adjustment; side installation is suitable for occasions with limited space and the need to fix the guide from the side, such as some narrow frame structure equipment; top installation is mainly used for specific equipment layouts, such as some inverted installation workbenches. When selecting the installation method, the equipment's structural design, maintenance convenience, and force conditions should be considered comprehensively to ensure that the guide is firmly installed and runs smoothly.
IV. Lubrication and Maintenance Considerations
Lubrication System Design: Good lubrication is the key to ensuring the long-term stable operation of linear guides. Different linear guide products are equipped with different lubrication systems, such as automatic lubrication systems, grease lubrication systems, and oil lubrication systems. Automatic lubrication systems can provide lubrication to the guide regularly and quantitatively, suitable for equipment running continuously for a long time, and can effectively reduce manual maintenance workload; grease lubrication systems are simple to operate and have good sealing performance, suitable for guide lubrication under general conditions, but grease needs to be added regularly; oil lubrication systems have good heat dissipation performance and are suitable for high-speed operation and high heat generation guides. During selection, the appropriate lubrication system should be selected according to the equipment's operating conditions and maintenance requirements.
Maintenance Convenience: Selecting easy-to-maintain linear guide products can reduce equipment operating costs and downtime. For example, the sealing structure of the guide should be easy to disassemble and clean, making it easy to remove accumulated dust and impurities; the oiling port of the lubrication system should be easy to operate, making it easy to add lubricant regularly; at the same time, the universality of the product is also important. Selecting commonly used guides on the market with easily accessible parts allows for quick replacement of parts when equipment malfunctions, shortening repair time.
V. Brand and Quality Assessment
Brand Reputation and Market Reputation: In the linear guide market, well-known brands often represent higher product quality and reliability. By consulting industry information, user reviews, and consulting industry professionals, understand the reputation and reputation of various brands in the market. For example, some internationally renowned brands, relying on their long-term accumulated technical research and development strength and strict quality control system, occupy a leading position in the field of high-precision and high-reliability linear guides, and their products are widely used in high-end manufacturing; while some emerging brands may have advantages in terms of price-performance ratio, but the stability of the product and long-term performance may need further verification.
Quality Certification and Test Reports: Formal linear guide products should have relevant quality certifications, such as ISO quality management system certification, CE certification, etc., these certifications are authoritative recognition of product quality and safety. At the same time, product test reports are also an important basis for evaluating quality, including precision test reports and load test reports. When purchasing, request the supplier to provide detailed quality certification documents and test reports to ensure that the selected guide products meet quality standards and technical requirements.
The selection of linear guides requires comprehensive consideration of application scenarios, load characteristics, precision requirements, size installation, lubrication maintenance, and brand quality. Only through comprehensive and detailed analysis and comparison can the most suitable linear guide products be selected to provide a solid guarantee for the efficient and stable operation of the equipment.
Welcome everyone to put forward different opinions. If you have any needs for related guide sliders, you can contact Maoming 24 hours online. Contact number: 15524757549 (WeChat synchronized)
Selection, equipment, guide rail, linear guide rail, installation, precision, lubrication
Previous
Latest News
Get a Free Consultancy

No. 39, Life Second Road, Dalian Economic and Technological Development Zone, 8-5
Copyright © 2025 Maoming Precision Machinery (Dalian) Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.




 2025-01-08
2025-01-08